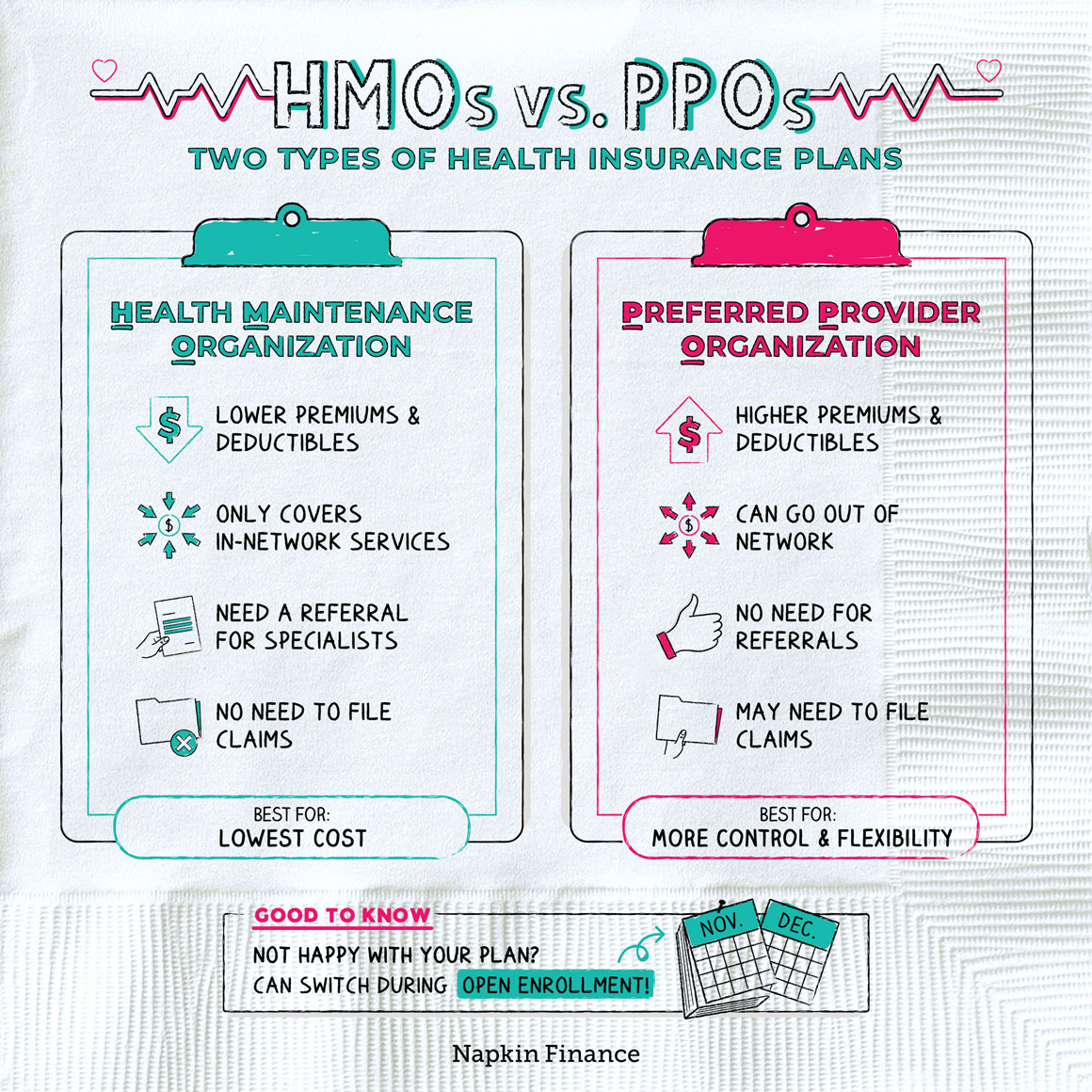
Navigating the Atlanta GA Health Insurance Market: A Guide for Consumers and Agents
Atlanta, Georgia, a bustling metropolis with a diverse population, presents a dynamic landscape for health insurance agents. Understanding this market requires navigating a complex web of demographics, competitive pressures, and regulatory compliance. From attracting clients with effective marketing strategies to mastering the intricacies of ACA compliance and various insurance plans, success hinges on a blend of sharp business acumen and deep product knowledge. This guide delves into the key aspects of operating as a health insurance agent in Atlanta, offering insights for both established professionals and those considering entering this competitive field. The Atlanta area’s diverse demographics, encompassing a wide range of ages, incomes, and health needs, demand a nuanced approach to health insurance sales. Competition is fierce, with established agencies and independent agents vying for market share. Successfully navigating this environment requires a robust understanding of the prevalent insurance providers, the intricacies of Georgia’s regulatory framework, and the unique challenges and opportunities presented by the city’s healthcare ecosystem. This includes a keen awareness of the Affordable Care Act’s implications and the evolving technological tools available to agents. Understanding the Atlanta GA Market The Atlanta metropolitan area presents a complex and dynamic market for health insurance agents, shaped by its diverse demographics, competitive landscape, and unique healthcare needs. Understanding these factors is crucial for success in this lucrative but challenging environment.The demographic profile of Atlanta significantly influences the demand for health insurance. The city boasts a large and growing population, encompassing a wide range of age groups, income levels, and ethnicities. A substantial portion of the population falls within the age bracket most susceptible to health issues and requiring comprehensive coverage. Furthermore, the presence of numerous large employers and a significant number of self-employed individuals contributes to the diverse insurance needs within the market. Specific segments, such as the rapidly expanding senior population and individuals with pre-existing conditions, represent key target markets for agents. The Competitive Landscape of Atlanta Health Insurance Agents Atlanta’s health insurance agent market is highly competitive. Numerous independent agents, large brokerage firms, and captive agents from major insurance providers operate within the city. This competition necessitates a strong understanding of the market, effective marketing strategies, and a commitment to providing exceptional client service to differentiate oneself. Successful agents often specialize in specific niches, such as Medicare supplemental plans or individual health insurance, to carve out a competitive advantage. The digital landscape plays a significant role, with online platforms and comparison websites increasingly influencing consumer choices, demanding agents possess robust online presence and digital marketing expertise. Prevalent Health Insurance Providers in the Atlanta Area Several major health insurance providers dominate the Atlanta market. These include national players like UnitedHealthcare, Anthem Blue Cross Blue Shield, Kaiser Permanente (in select areas), and Cigna. Additionally, several regional and smaller insurers offer coverage within the area, creating a diverse range of plan options and pricing structures. The presence of these large and established providers often means intense competition for agents seeking to partner with them and access their extensive networks. The prevalence of these large providers highlights the importance for agents to possess a comprehensive understanding of their respective product offerings and network capabilities. Challenges and Opportunities for Health Insurance Agents in Atlanta Health insurance agents in Atlanta face several challenges. The complexity of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the constantly evolving regulatory landscape require ongoing professional development and a deep understanding of compliance requirements. The increasing use of technology and online platforms necessitates adaptation and the adoption of digital marketing strategies. Furthermore, effectively navigating the competitive landscape requires a keen understanding of the market dynamics and the ability to differentiate oneself through exceptional customer service and specialized expertise. However, the significant population size, diverse demographics, and substantial demand for health insurance create ample opportunities for skilled and knowledgeable agents. The increasing focus on preventative care and wellness programs, coupled with the growth of the senior population, presents specific opportunities for agents specializing in these areas. The constant need for personalized guidance and support in navigating the complexities of health insurance continues to be a major advantage for agents capable of delivering excellent client service. Client Acquisition Strategies Securing a robust client base is paramount for any health insurance agent operating in the competitive Atlanta market. A multifaceted approach, leveraging both digital and traditional marketing strategies, is crucial for achieving sustainable growth. This plan Artikels key strategies for client acquisition, relationship building, and network development within the Atlanta community. Marketing Plan for Atlanta A comprehensive marketing plan should encompass both online and offline channels to reach the diverse population of Atlanta. The following table Artikels key channels and associated cost considerations. Note that costs are estimates and can vary significantly based on campaign scope and duration. Marketing Channel Description Estimated Cost (Annual) Target Audience Digital Marketing (/SEM) Search engine optimization () to improve organic search ranking and search engine marketing (SEM) through paid advertising on Google and other search engines. $5,000 $20,000 Individuals actively searching for health insurance online. Social Media Marketing (Facebook, Instagram) Targeted advertising campaigns on Facebook and Instagram to reach specific demographics and interests within the Atlanta area. $3,000 $10,000 Younger demographics, individuals interested in health and wellness. Email Marketing Building an email list and sending targeted email campaigns to nurture leads and promote services. $1,000 $5,000 Existing and potential clients. … Read more