Navigating the complex world of health insurance can be daunting, especially when faced with the decision between a PPO and an HMO plan. Both offer coverage, but their structures and features can significantly impact your healthcare experience and costs. This guide will delve into the key differences between PPO and HMO plans, helping you understand the nuances of each and make an informed decision for your individual needs.
From network structures and cost-sharing mechanisms to flexibility in choosing providers and the referral process, we’ll examine the critical factors that differentiate these plans. We’ll also explore real-world scenarios, cost considerations, and future trends in the healthcare landscape that may influence your choice. Ultimately, this comprehensive guide aims to empower you with the knowledge to select the health insurance plan that best aligns with your healthcare priorities and financial realities.
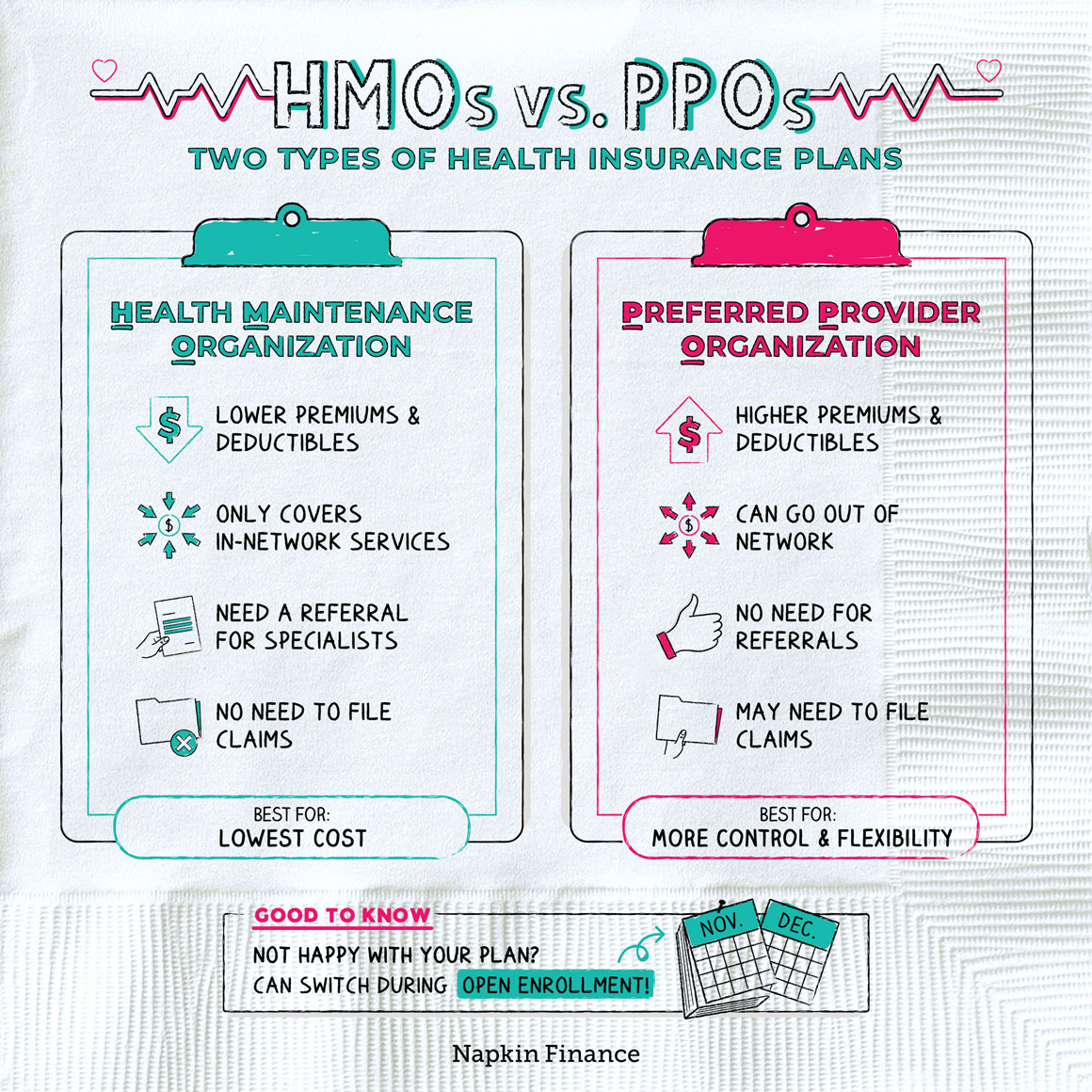
Understanding PPO and HMO Insurance
Choosing the right health insurance plan can be overwhelming, especially with the various options available. Two popular choices are Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) and Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs). While both offer coverage for medical expenses, they differ in their structure and how they handle costs. Understanding the core principles of each plan is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your individual needs and budget.
PPO Insurance Plans
PPO plans provide flexibility and wider network access compared to HMOs. They allow you to choose your healthcare providers from a broader network, including specialists and hospitals outside the plan’s designated network. While you pay a higher premium for this flexibility, you can opt for out-of-network providers if you prefer. However, using out-of-network providers incurs higher costs and requires pre-authorization.
HMO Insurance Plans
HMO plans prioritize cost-effectiveness and preventive care. They typically have lower premiums compared to PPOs but restrict you to a specific network of providers. This means you need to select a primary care physician (PCP) within the network who acts as your gatekeeper for accessing specialists. HMO plans emphasize preventive care and encourage regular checkups to manage health conditions proactively.
Definition of a Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
A PPO is a type of health insurance plan that allows you to choose your healthcare providers from a wide network. You can visit in-network providers without needing referrals, but you can also choose out-of-network providers at a higher cost.
Definition of a Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
An HMO is a type of health insurance plan that emphasizes cost-effectiveness and preventive care. It typically requires you to select a primary care physician (PCP) within the network and obtain referrals to see specialists.
Key Differences between PPO and HMO
PPO and HMO are two popular types of health insurance plans, each offering different benefits and coverage structures. While both aim to provide healthcare access, understanding their key differences is crucial for making an informed decision about the plan that best suits your individual needs.
Network Structures
The network structure is a fundamental difference between PPO and HMO plans. It defines the healthcare providers, such as hospitals, doctors, and specialists, who are contracted with the insurance company to provide services at negotiated rates.
- PPO (Preferred Provider Organization): PPO plans offer a wider network of healthcare providers than HMOs. This means you have more flexibility in choosing doctors and hospitals, even if they are outside your network. However, choosing an in-network provider typically results in lower out-of-pocket costs.
- HMO (Health Maintenance Organization): HMO plans have a more limited network of healthcare providers. You must choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the network, who will act as your gatekeeper for referrals to specialists. Choosing an out-of-network provider is typically not covered or covered at a significantly lower rate, making it less appealing for most individuals.
Cost-Sharing Structures
Cost-sharing refers to the financial responsibility you bear for your healthcare expenses, including deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. The cost-sharing structure can vary significantly between PPO and HMO plans.
- PPO: PPO plans generally have higher deductibles than HMOs. This means you’ll need to pay more out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. However, PPOs typically have lower copays for in-network services. This means you’ll pay less for each visit or service within the network.
- HMO: HMO plans generally have lower deductibles than PPOs. This means you’ll pay less out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage begins. However, HMOs may have higher copays for in-network services. This means you’ll pay more for each visit or service within the network.
Flexibility in Choosing Healthcare Providers
Flexibility in choosing healthcare providers is a crucial factor for many individuals. PPO and HMO plans differ significantly in this aspect.
- PPO: PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. You can choose a doctor or hospital outside your network, though you’ll generally pay higher out-of-pocket costs. This flexibility is particularly appealing to individuals who prefer to maintain their existing relationships with their healthcare providers or who need specialized care that may not be available within the network.
- HMO: HMO plans offer less flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. You must select a PCP within the network, who will act as your gatekeeper for referrals to specialists. This can be limiting for individuals who have established relationships with providers outside the network or who prefer to have more control over their healthcare decisions.
Approval Process for Referrals
Referrals are necessary for accessing specialized healthcare services, such as seeing a specialist or undergoing a particular medical procedure. The referral process differs significantly between PPO and HMO plans.
- PPO: PPO plans generally have a more relaxed referral process. You may be able to see a specialist without a referral, though you’ll likely pay higher out-of-pocket costs. This flexibility can be beneficial for individuals who need prompt access to specialized care.
- HMO: HMO plans typically require a referral from your PCP before you can see a specialist. This process can add time and complexity to accessing specialized care. However, it aims to ensure that your care is coordinated and cost-effective.
Choosing the Right Plan
Selecting the right health insurance plan can be a daunting task, especially when faced with the choice between a PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) and an HMO (Health Maintenance Organization). Both plans offer coverage, but they differ significantly in terms of cost, flexibility, and access to healthcare providers. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision that best suits your individual needs and circumstances.
PPO Plans: Advantages and Disadvantages
PPO plans offer greater flexibility than HMOs, allowing you to choose your healthcare providers from a wider network. This flexibility comes with a higher premium cost, and you may face higher out-of-pocket expenses for services outside the preferred network.
- Advantages:
- Greater Flexibility: PPOs allow you to see any doctor within the network, including specialists, without needing a referral. This can be particularly beneficial for those who prefer to have a choice in their healthcare providers.
- Out-of-Network Coverage: While you’ll pay more, PPOs typically offer some coverage for services received from providers outside the network. This can be helpful if you need to see a specialist who is not in your network or if you find yourself in an emergency situation far from home.
- Higher Premiums: PPOs generally have higher monthly premiums than HMOs due to their greater flexibility and out-of-network coverage options.
- Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs: While PPOs provide out-of-network coverage, you’ll typically pay a higher coinsurance percentage and higher deductibles for services received outside the preferred network. This can lead to significant out-of-pocket expenses.
HMO Plans: Advantages and Disadvantages
HMO plans are known for their lower premiums and emphasis on preventive care. However, they offer less flexibility in terms of provider choice and may require referrals for specialist care.
- Advantages:
- Lower Premiums: HMOs typically have lower monthly premiums than PPOs, making them a more affordable option for budget-conscious individuals. This is because HMOs have a more tightly controlled network of providers and often focus on preventive care, which can reduce overall healthcare costs.
- Emphasis on Preventive Care: HMOs generally encourage preventive care services, such as annual checkups and screenings, which can help identify health issues early and potentially reduce the need for more expensive treatments later.
- Limited Provider Choice: HMOs have a narrower network of providers than PPOs, which can limit your choice of doctors and specialists. You may need to find a provider within the network, even if they are not the most convenient or the best fit for your needs.
- Referral Requirements: HMOs often require referrals from your primary care physician to see specialists. This can be a hassle, especially if you need to see a specialist urgently.
PPO vs. HMO: Key Features
| Feature | PPO | HMO |
|---|---|---|
| Network | Wider network, including out-of-network coverage | Narrower network, limited out-of-network coverage |
| Cost | Higher premiums, potentially higher out-of-pocket costs | Lower premiums, potentially lower out-of-pocket costs |
| Flexibility | Greater flexibility in provider choice, no referral required | Less flexibility, referrals often required |
| Preventive Care | May or may not emphasize preventive care | Typically emphasizes preventive care |
PPO and HMO in Practice
Understanding the differences between PPO and HMO plans is crucial, but seeing how they work in real-world scenarios can make the decision even clearer. Let’s explore some situations where each plan might be more advantageous.
PPO Advantages in Practice
A PPO plan offers more flexibility, allowing you to choose your healthcare providers, even outside the network. This can be particularly beneficial in the following situations:
- Specialized Care: If you require a specialist not included in your HMO’s network, a PPO plan lets you seek care from a specialist of your choice, even if they are out-of-network. This flexibility is essential for conditions requiring specialized expertise.
- Moving or Traveling: When you relocate or travel, a PPO plan provides coverage even if you need to see a doctor outside your original network area. This is particularly important for frequent travelers or those who move frequently.
- Unexpected Emergencies: In emergencies, a PPO plan offers the security of knowing you can access care at any hospital, even if it’s not in your network. This eliminates the worry of finding an in-network facility during a crisis.
- Personal Preferences: Some individuals prefer to have a wider choice of doctors and hospitals, regardless of network restrictions. PPO plans allow for this personalized approach to healthcare.
HMO Advantages in Practice
While PPOs offer flexibility, HMOs often provide lower premiums and emphasize preventative care. Here are some scenarios where an HMO might be the better choice:
- Cost-Consciousness: If you prioritize affordability and are generally healthy, an HMO plan’s lower premiums and co-pays can be attractive. You’ll likely pay less for routine care, but you’ll need to stay within the network for most services.
- Preventative Care Focus: HMOs often emphasize preventative care, with lower costs for screenings and wellness visits. This can be beneficial for individuals seeking to proactively manage their health.
- Limited Healthcare Needs: If your healthcare needs are typically limited to routine checkups and basic services, an HMO plan can be a cost-effective option. You’ll likely find all the essential services within your network.
Choosing the Right Plan: A Hypothetical Scenario
Imagine you’re a young professional in good health, with a stable job and limited healthcare needs. You prioritize affordability and prefer preventative care. You also live in a city with a strong network of doctors and hospitals. In this case, an HMO plan could be a suitable choice. You’d enjoy lower premiums and benefit from the focus on preventative care, while still having access to quality healthcare within your network.
However, if you have a chronic condition requiring specialized care or frequently travel for work, a PPO plan might be more suitable. The flexibility to choose specialists outside your network and access care across different regions could be valuable.
Ultimately, the best plan depends on your individual circumstances, health needs, and priorities.
PPO and HMO: Beyond the Basics
Beyond the core differences, understanding the nuances of PPO and HMO plans can help you make an informed decision. This section delves into specific aspects of these plans that go beyond the initial comparison.
Out-of-Network Coverage in PPO Plans
PPO plans offer the flexibility of seeking care from providers outside their network. However, this out-of-network coverage comes with a higher cost.
- Higher Co-pays and Deductibles: When you use out-of-network providers, you’ll typically face significantly higher co-pays and deductibles compared to in-network care. This means you’ll be responsible for a larger share of the medical costs.
- Pre-authorization Requirements: Many PPO plans require pre-authorization for out-of-network services. This means you’ll need to get approval from your insurer before receiving care, which can add complexity to the process.
- Limited Coverage: Some PPO plans may limit the amount of out-of-network coverage they provide. This could mean you’re responsible for a larger portion of the costs or that certain services are not covered at all.
It’s crucial to carefully review your PPO plan’s out-of-network coverage details to understand the financial implications.
The Role of Primary Care Physicians (PCPs) in HMO Plans
HMO plans emphasize a coordinated approach to healthcare, with the PCP serving as the central point of contact.
- Gatekeeper to Specialists: PCPs act as gatekeepers, referring you to specialists only when deemed necessary. This system aims to reduce unnecessary testing and procedures, potentially lowering healthcare costs.
- Care Coordination: PCPs are responsible for coordinating your care across different healthcare providers. They can ensure continuity of care and help avoid duplicate testing or conflicting treatments.
- Emphasis on Preventive Care: HMOs often encourage preventive care through their PCPs. This can include regular checkups, screenings, and vaccinations, which can help detect health issues early and improve overall health.
The PCP’s role in HMO plans can contribute to a more proactive and coordinated approach to healthcare, but it’s essential to choose a PCP who aligns with your healthcare needs and preferences.
Types of HMO Plans
HMO plans are offered in various models, each with its own structure and approach to healthcare delivery.
- Staff Model HMOs: In this model, the HMO directly employs physicians and other healthcare providers. This allows for greater control over care delivery and potential cost savings. However, it may limit the choice of providers.
- Group Model HMOs: Group model HMOs contract with a group of physicians or healthcare providers to deliver services. This allows for a wider range of provider options compared to staff model HMOs.
- Network Model HMOs: Network model HMOs contract with multiple independent physician groups or healthcare providers. This offers the most extensive provider choice but may require more coordination between different providers.
Understanding the specific model of your HMO plan can help you navigate its structure and make informed decisions about your healthcare.
Cost Considerations for PPO and HMO
Choosing between a PPO and HMO plan often boils down to cost. Both plans have their own unique structures for managing healthcare expenses, influencing your overall out-of-pocket costs. Understanding the key cost components, such as premiums, deductibles, and copays, can help you make an informed decision.
Premiums
Premiums are the monthly payments you make to maintain your health insurance coverage. PPO plans generally have higher premiums than HMO plans. This is because PPOs offer more flexibility and broader provider networks, which come at a cost. For instance, a PPO plan may have a monthly premium of $400, while a comparable HMO plan might cost $350.
Deductibles
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. PPO plans typically have higher deductibles than HMO plans. This means you’ll need to pay a larger amount upfront before your insurance starts covering your healthcare expenses. For example, a PPO plan may have a deductible of $2,000, while an HMO plan might have a deductible of $1,000.
Copays
Copays are fixed amounts you pay for specific healthcare services, such as doctor’s visits or prescriptions. Both PPO and HMO plans have copays, but the amounts can vary. PPO plans often have lower copays than HMO plans, making them more appealing for individuals who anticipate frequent doctor visits.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses
PPO plans generally have higher out-of-pocket expenses than HMO plans. This is because PPO plans often have higher deductibles and lower copays, leading to greater upfront costs. For example, a PPO plan might require you to pay $2,000 in deductibles before your insurance coverage starts, while an HMO plan might have a $1,000 deductible. However, PPO plans often have lower copays, which can help offset the higher deductibles.
Health Needs and Plan Choice
Your health needs and preferences should be the primary factors when choosing between a PPO and HMO plan. Understanding how each plan type addresses different health situations can help you make an informed decision.
Matching Health Needs to Plan Types
The type of health coverage you need depends on your specific health needs and the frequency with which you seek medical care.
- Routine Care and Preventative Services: HMO plans typically offer lower premiums and co-pays for routine checkups, screenings, and preventative services. They often have strong networks of primary care physicians, making it easier to find a provider within your network.
- Specialized Care: PPO plans provide greater flexibility in choosing specialists and hospitals, even outside the network. This can be beneficial for individuals with complex medical conditions requiring specialized care or who prefer to see a specific provider outside the HMO network.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing conditions might prefer a PPO plan, as these plans generally have fewer restrictions on coverage for pre-existing conditions. While both PPO and HMO plans must comply with the Affordable Care Act’s (ACA) regulations regarding pre-existing conditions, PPOs may offer more comprehensive coverage.
- Travel and Out-of-State Care: If you travel frequently or expect to receive medical care outside your state, a PPO plan with broader coverage may be more suitable. PPO plans often have larger networks and out-of-network coverage, allowing you to access care in different regions.
Evaluating Individual Healthcare Needs
To determine the best plan for you, consider the following factors:
- Frequency of Medical Visits: If you require frequent medical care, an HMO plan with lower co-pays and deductibles may be more cost-effective. However, if you generally have good health and only require occasional care, a PPO plan might be more affordable.
- Specific Medical Needs: If you have a chronic condition or require specialized care, a PPO plan offering broader provider choices and greater flexibility may be more beneficial. Conversely, if your needs are primarily routine checkups and preventative care, an HMO plan might be a better fit.
- Budget and Cost Considerations: PPO plans generally have higher premiums but lower co-pays and deductibles. HMO plans often have lower premiums but may have higher co-pays and deductibles. Carefully compare the costs associated with each plan type to determine which fits your budget.
- Provider Network: Examine the provider networks of both PPO and HMO plans to ensure that your preferred doctors and hospitals are included. A plan with a limited network might restrict your access to care, especially if you have specific medical needs.
Impact of Pre-existing Conditions
Pre-existing conditions can significantly influence your plan choice. While the ACA prohibits health insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based solely on pre-existing conditions, some differences in coverage and cost can still exist.
- PPOs generally offer greater flexibility in provider choice and out-of-network coverage, which can be beneficial for individuals with pre-existing conditions requiring specialized care or specific providers. However, PPOs may have higher premiums and deductibles.
- HMOs may have more limited networks and stricter requirements for coverage, but they often offer lower premiums and co-pays for routine care. Individuals with pre-existing conditions should carefully review the HMO plan’s coverage details to ensure their specific needs are met.
Navigating the Healthcare System
Understanding the intricacies of insurance providers and health insurance exchanges is crucial for navigating the healthcare system effectively. This section will provide insights into their roles and offer practical tips for understanding and maximizing your insurance coverage.
Insurance Providers and Health Insurance Exchanges
Insurance providers play a pivotal role in the healthcare system by offering various health insurance plans. These plans cover a range of medical expenses, from doctor’s visits to hospital stays. Health insurance exchanges, on the other hand, serve as online marketplaces where individuals can compare and enroll in health insurance plans.
Understanding and Navigating Insurance Coverage
Navigating the complexities of insurance coverage can be challenging, but understanding key concepts and strategies can empower you to make informed decisions.
- Review your Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC): This document Artikels the essential details of your plan, including covered services, deductibles, copayments, and out-of-pocket maximums.
- Familiarize yourself with your network: Your insurance plan’s network comprises healthcare providers (doctors, hospitals, etc.) with whom the insurer has negotiated discounted rates. Utilizing in-network providers will generally result in lower out-of-pocket costs.
- Understand your plan’s coverage for preventive care: Many plans cover preventive services, such as annual checkups and screenings, at no cost. Taking advantage of these services can help detect potential health issues early on.
- Be aware of your out-of-pocket maximum: This is the maximum amount you’ll pay for covered healthcare services in a given year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance plan covers 100% of eligible expenses.
Resources and Tools for Research and Comparison
Several resources and tools are available to help you research and compare health insurance plans.
- Health Insurance Marketplace: This website, operated by the federal government, allows individuals to compare plans, estimate costs, and enroll in coverage. It offers a wide range of plans from different insurers.
- State-based insurance marketplaces: Many states have their own insurance marketplaces, which may offer additional plan options and resources.
- Insurance company websites: Most insurance providers have detailed information about their plans on their websites, including coverage details, cost estimates, and provider networks.
- Independent insurance brokers: These brokers can provide personalized guidance and help you compare plans from multiple insurers.
PPO and HMO: Future Trends
The healthcare landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies, regulations, and consumer preferences shaping the future of healthcare delivery. This dynamic environment will undoubtedly influence the trajectory of PPO and HMO plans, leading to potential changes and adaptations.
Impact of Healthcare Reform
Healthcare reform initiatives, such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA), have already had a significant impact on PPO and HMO plans. The ACA aimed to expand health insurance coverage and promote affordability, leading to changes in plan design and benefit structures. For instance, the ACA mandated essential health benefits, such as preventive care and maternity care, which are now included in most PPO and HMO plans. This has resulted in a more standardized set of benefits across different plan types.
The ACA has led to a greater emphasis on preventive care and wellness programs, which are often integrated into both PPO and HMO plans.
The ACA also introduced cost-sharing mechanisms, such as deductibles and copayments, which have become more prevalent in both PPO and HMO plans. These cost-sharing provisions aim to encourage consumers to make more informed healthcare decisions and reduce overall healthcare spending.
Emerging Models of Healthcare Delivery
The rise of value-based care models, which emphasize quality outcomes and cost-effectiveness, is influencing the design of PPO and HMO plans. These models incentivize providers to deliver high-quality care at lower costs, shifting the focus from fee-for-service to value-based reimbursement.
- Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs): ACOs are groups of providers who coordinate care for a defined population of patients, taking responsibility for both quality and cost. HMOs are increasingly partnering with ACOs to integrate care delivery and manage costs effectively.
- Direct Primary Care (DPC): DPC models offer patients unlimited access to primary care services for a fixed monthly fee, eliminating the need for traditional insurance plans. While DPC is still a relatively new model, it may gain traction in the future, potentially influencing the design of PPO and HMO plans.
- Telemedicine: The use of technology to deliver healthcare services remotely is rapidly expanding. PPO and HMO plans are increasingly incorporating telemedicine benefits, allowing patients to access care from the comfort of their homes.
As these models become more prevalent, PPO and HMO plans may evolve to incorporate features that align with value-based care principles.
Future Trends in PPO and HMO Plans
The future of PPO and HMO plans is likely to be characterized by several trends:
- Increased Consumer Choice and Flexibility: Consumers are demanding more control over their healthcare decisions, and insurance plans are responding by offering more flexible options, such as high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) with health savings accounts (HSAs). This trend may lead to a blurring of the lines between PPO and HMO plans, as insurers offer more customized options.
- Focus on Wellness and Prevention: The emphasis on preventive care and wellness is likely to continue, with PPO and HMO plans offering incentives for healthy behaviors, such as discounts on gym memberships or wellness programs.
- Greater Transparency and Data-Driven Decision-Making: Consumers are increasingly demanding transparency in healthcare costs and outcomes. Insurance plans are responding by providing more data and tools to help consumers make informed decisions. This trend is likely to drive the development of data-driven tools that personalize plan recommendations and predict healthcare needs.
- Integration of Technology: Technology will continue to play a significant role in healthcare delivery, and PPO and HMO plans will need to adapt to these changes. This includes incorporating telehealth services, wearable technology, and digital health tools into their offerings.
The future of PPO and HMO plans will likely be characterized by a greater emphasis on personalization, transparency, and technology.
Additional Considerations for PPO and HMO
While both PPO and HMO plans offer coverage, they come with distinct advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these nuances is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your individual needs and financial situation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PPO Plans
PPO plans offer flexibility and broader access to healthcare providers. However, they typically come with higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
- Advantages:
- Greater Provider Choice: PPOs allow you to see any in-network provider without needing a referral. This means you have a wider range of specialists and healthcare facilities to choose from.
- Out-of-Network Coverage: PPOs offer some coverage for out-of-network services, though at a higher cost. This provides a safety net if you need to see a specialist who is not in your plan’s network.
- No Gatekeeper: You don’t need a referral from your primary care physician to see specialists, making access to specialized care more convenient.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher Premiums: PPOs generally have higher monthly premiums compared to HMOs due to the broader coverage they offer.
- Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs: You may face higher copayments, deductibles, and coinsurance with PPOs, particularly for out-of-network services.
- Less Comprehensive Coverage: While PPOs offer more provider choice, they may not cover all services as comprehensively as HMOs, especially preventive care.
Advantages and Disadvantages of HMO Plans
HMO plans typically have lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs but offer less flexibility in choosing providers.
- Advantages:
- Lower Premiums: HMOs generally have lower monthly premiums than PPOs due to their more restricted network and emphasis on preventive care.
- Lower Out-of-Pocket Costs: HMOs often have lower copayments, deductibles, and coinsurance compared to PPOs, making them more budget-friendly for routine healthcare.
- Comprehensive Coverage: HMOs typically cover a wide range of preventive services, including screenings and vaccinations, with minimal or no out-of-pocket costs.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited Provider Choice: HMOs require you to choose a primary care physician within their network and obtain referrals to see specialists. This can limit your choice of healthcare providers.
- No Out-of-Network Coverage: HMOs generally do not cover out-of-network services, meaning you’ll have to pay the full cost for care outside the network.
- Potential for Longer Wait Times: The restricted provider network within HMOs can lead to longer wait times for appointments, especially for specialists.
Effective Utilization of PPO Benefits
Maximizing the benefits of a PPO plan requires understanding its specific terms and conditions and making informed choices regarding healthcare providers and services.
- Negotiate Rates: PPOs often allow you to negotiate rates with providers, particularly for elective procedures or services not covered by insurance.
- Utilize Preventive Care: PPOs typically cover preventive services like screenings and vaccinations at a lower cost or even free of charge. Taking advantage of these services can help prevent health issues and reduce healthcare expenses in the long run.
- Consider Out-of-Network Options Carefully: While PPOs offer out-of-network coverage, it’s crucial to weigh the potential cost savings against the higher out-of-pocket expenses and limited coverage.
Effective Utilization of HMO Benefits
To fully utilize the benefits of an HMO plan, it’s essential to work closely with your primary care physician and follow their recommendations for care.
- Build a Relationship with Your Primary Care Physician: Establishing a strong relationship with your primary care physician is crucial for effective healthcare management within an HMO. They can provide guidance on preventive care, referrals to specialists, and overall health management.
- Take Advantage of Preventive Care: HMOs often emphasize preventive care and provide comprehensive coverage for screenings and vaccinations. This can help identify health issues early and reduce the need for more expensive treatments later.
- Utilize Telemedicine: Many HMOs offer telemedicine services, which can provide convenient and affordable access to healthcare professionals for routine check-ups, consultations, and even certain treatments.
Understanding Plan Terms and Conditions
Each health insurance plan, whether PPO or HMO, has its unique terms and conditions. It’s crucial to thoroughly understand these details before making a decision.
- Network: Review the provider network carefully to ensure that your preferred doctors and specialists are included.
- Coverage: Understand the specific services covered by the plan, including deductibles, copayments, coinsurance, and out-of-pocket maximums.
- Exclusions: Familiarize yourself with the services not covered by the plan, such as experimental treatments or certain cosmetic procedures.
- Prior Authorization: Some plans require prior authorization for certain procedures or treatments. Ensure you understand the process and requirements.
Conclusive Thoughts
In the end, the decision between a PPO and an HMO hinges on your individual healthcare needs, preferences, and financial situation. By carefully evaluating your circumstances, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each plan type, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, you can confidently choose the insurance plan that provides the most comprehensive and cost-effective coverage for you and your family.