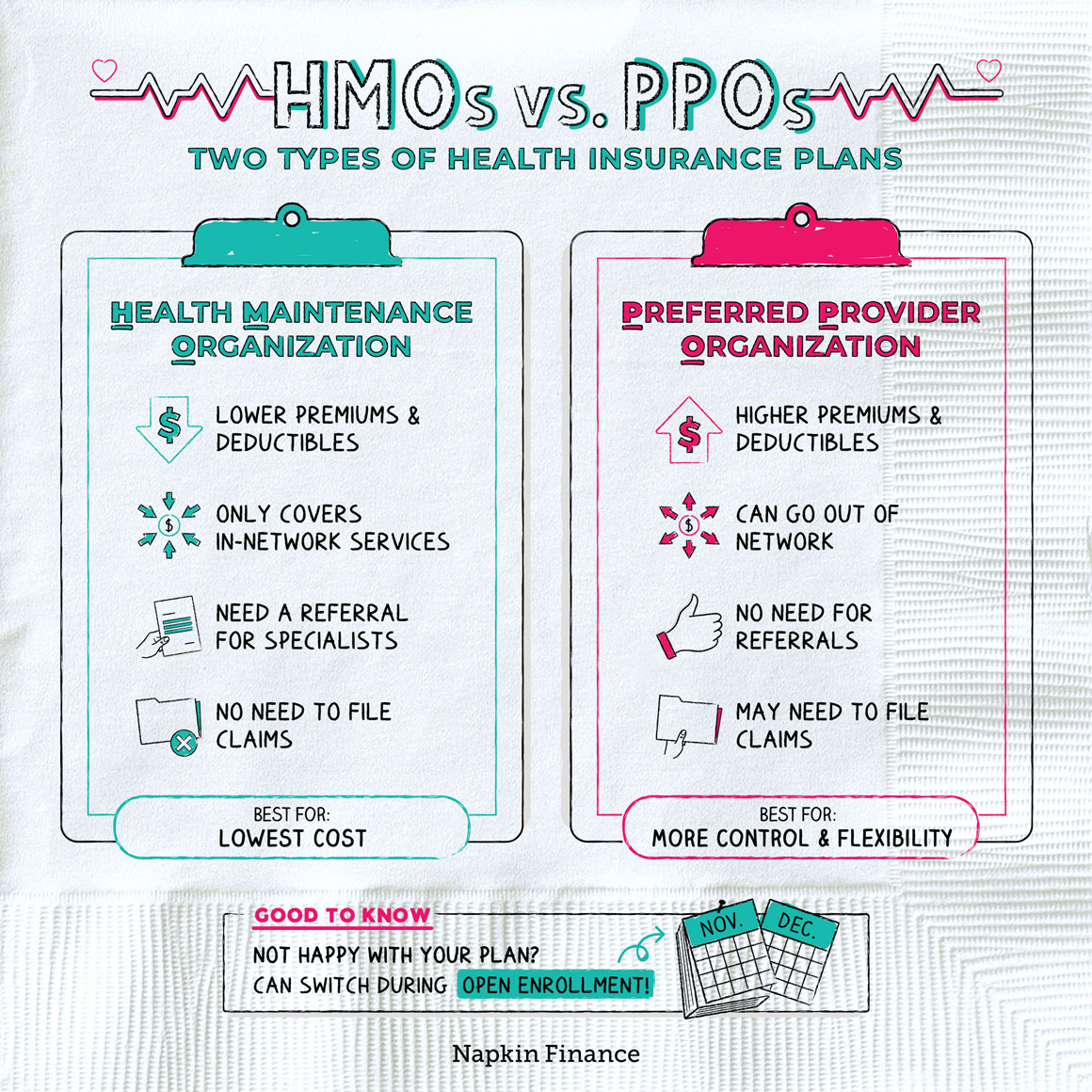
PPO vs. HMO Insurance: Choosing the Right Health Plan for You
Navigating the complex world of health insurance can be daunting, especially when faced with the decision between a PPO and an HMO plan. Both offer coverage, but their structures and features can significantly impact your healthcare experience and costs. This guide will delve into the key differences between PPO and HMO plans, helping you understand the nuances of each and make an informed decision for your individual needs. From network structures and cost-sharing mechanisms to flexibility in choosing providers and the referral process, we’ll examine the critical factors that differentiate these plans. We’ll also explore real-world scenarios, cost considerations, and future trends in the healthcare landscape that may influence your choice. Ultimately, this comprehensive guide aims to empower you with the knowledge to select the health insurance plan that best aligns with your healthcare priorities and financial realities. Understanding PPO and HMO Insurance Choosing the right health insurance plan can be overwhelming, especially with the various options available. Two popular choices are Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) and Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs). While both offer coverage for medical expenses, they differ in their structure and how they handle costs. Understanding the core principles of each plan is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your individual needs and budget. PPO Insurance Plans PPO plans provide flexibility and wider network access compared to HMOs. They allow you to choose your healthcare providers from a broader network, including specialists and hospitals outside the plan’s designated network. While you pay a higher premium for this flexibility, you can opt for out-of-network providers if you prefer. However, using out-of-network providers incurs higher costs and requires pre-authorization. HMO Insurance Plans HMO plans prioritize cost-effectiveness and preventive care. They typically have lower premiums compared to PPOs but restrict you to a specific network of providers. This means you need to select a primary care physician (PCP) within the network who acts as your gatekeeper for accessing specialists. HMO plans emphasize preventive care and encourage regular checkups to manage health conditions proactively. Definition of a Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) A PPO is a type of health insurance plan that allows you to choose your healthcare providers from a wide network. You can visit in-network providers without needing referrals, but you can also choose out-of-network providers at a higher cost. Definition of a Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) An HMO is a type of health insurance plan that emphasizes cost-effectiveness and preventive care. It typically requires you to select a primary care physician (PCP) within the network and obtain referrals to see specialists. Key Differences between PPO and HMO PPO and HMO are two popular types of health insurance plans, each offering different benefits and coverage structures. While both aim to provide healthcare access, understanding their key differences is crucial for making an informed decision about the plan that best suits your individual needs. Network Structures The network structure is a fundamental difference between PPO and HMO plans. It defines the healthcare providers, such as hospitals, doctors, and specialists, who are contracted with the insurance company to provide services at negotiated rates. PPO (Preferred Provider Organization): PPO plans offer a wider network of healthcare providers than HMOs. This means you have more flexibility in choosing doctors and hospitals, even if they are outside your network. However, choosing an in-network provider typically results in lower out-of-pocket costs. HMO (Health Maintenance Organization): HMO plans have a more limited network of healthcare providers. You must choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the network, who will act as your gatekeeper for referrals to specialists. Choosing an out-of-network provider is typically not covered or covered at a significantly lower rate, making it less appealing for most individuals. Cost-Sharing Structures Cost-sharing refers to the financial responsibility you bear for your healthcare expenses, including deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. The cost-sharing structure can vary significantly between PPO and HMO plans. PPO: PPO plans generally have higher deductibles than HMOs. This means you’ll need to pay more out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. However, PPOs typically have lower copays for in-network services. This means you’ll pay less for each visit or service within the network. HMO: HMO plans generally have lower deductibles than PPOs. This means you’ll pay less out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage begins. However, HMOs may have higher copays for in-network services. This means you’ll pay more for each visit or service within the network. Flexibility in Choosing Healthcare Providers Flexibility in choosing healthcare providers is a crucial factor for many individuals. PPO and HMO plans differ significantly in this aspect. PPO: PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. You can choose a doctor or hospital outside your network, though you’ll generally pay higher out-of-pocket costs. This flexibility is particularly appealing to individuals who prefer to maintain their existing relationships with their healthcare providers or who need specialized care that may not be available within the network. HMO: HMO plans offer less flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. You must select a PCP within the network, who will act as your gatekeeper for referrals to specialists. This can be limiting for individuals who have established relationships with providers outside the network or who prefer to have more control over their healthcare decisions. Approval Process for Referrals Referrals are necessary for accessing specialized healthcare services, such as seeing a specialist or undergoing a particular medical procedure. The referral process differs significantly between PPO and HMO plans. PPO: PPO plans generally have a more relaxed referral process. You may be able to see a specialist without a referral, though you’ll likely pay higher out-of-pocket costs. This flexibility can be beneficial for individuals who need prompt access to specialized care. HMO: HMO plans typically require a referral from your PCP before you can see a specialist. This process can add time and complexity to accessing specialized care. However, it aims to ensure that your care is coordinated and cost-effective. Choosing the Right Plan Selecting the right health insurance plan can be a daunting task, especially when faced with the choice between a PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) and an HMO (Health Maintenance Organization). Both plans offer coverage, but they differ significantly in terms of cost, flexibility, and access to healthcare providers. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision that best suits your individual needs and circumstances. PPO Plans: Advantages and Disadvantages PPO plans offer greater flexibility than HMOs, allowing you to choose your healthcare providers from a wider network. This flexibility comes with a higher premium cost, and you may face higher out-of-pocket expenses for services outside the preferred network. Advantages: Greater Flexibility: PPOs allow you to see any doctor within the network, including specialists, without needing a referral. This can be particularly beneficial for those who prefer to have a choice in their healthcare providers. Out-of-Network Coverage: While you’ll pay more, PPOs typically offer some coverage for services received from providers outside the network. This can be helpful if you need to see a specialist who is not in your network or if you find yourself in an emergency situation far from home. Disadvantages: Higher Premiums: PPOs generally have higher monthly premiums than HMOs due to their greater flexibility and out-of-network coverage options. Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs: While PPOs provide out-of-network coverage, you’ll typically pay a higher coinsurance percentage and higher deductibles for services received outside the preferred network. This can lead to significant out-of-pocket expenses. HMO Plans: Advantages and Disadvantages HMO plans are known for their lower premiums and emphasis on preventive care. However, they offer less flexibility in terms of provider choice and may require referrals for specialist care. Advantages: Lower Premiums: HMOs typically have lower monthly premiums than PPOs, making them a more affordable option for budget-conscious individuals. This is because HMOs have a more tightly controlled network of providers and often focus on preventive care, which can reduce overall healthcare costs. … Read more